Overview: GIS in Saudi Urban Development
National-Level Geospatial Coordination
At the heart of GIS innovation in Saudi Arabia is the General Authority for Survey and Geospatial Information (GASGI) and its National Geospatial Center. This institution centralizes high-resolution mapping data to support sectors such as public safety, transportation, water management, and urban planning. Real-time geospatial dashboards are actively used for traffic optimization, waste management, air-quality monitoring, and even managing pilgrim movements during Hajj.
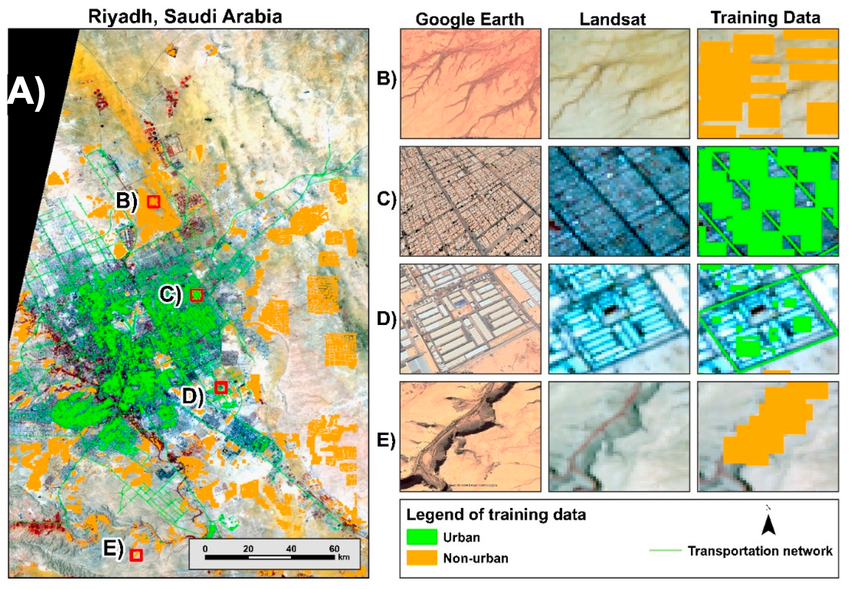
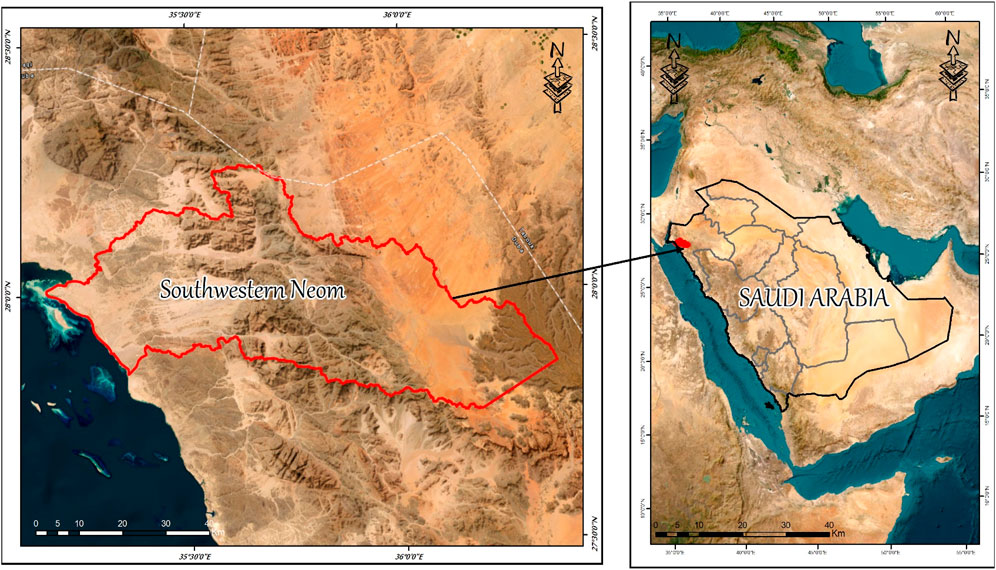
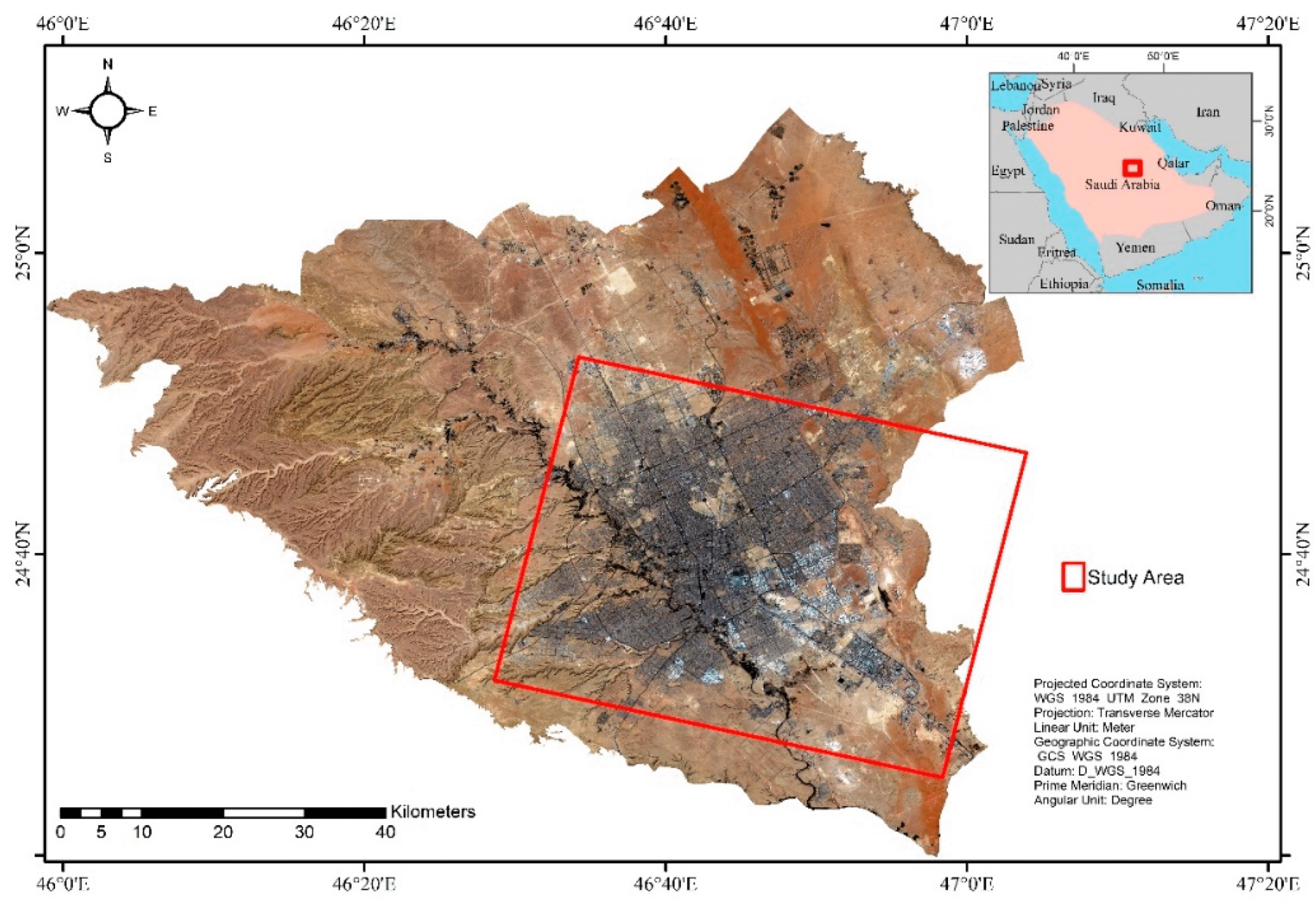
Here are some GIS-based visualizations related to Saudi Arabia’s urban development strategies—including land-use change maps, site-specific models, and geospatial frameworks that help illustrate the role of GIS in planning across the Kingdom.
Smart and Sustainable Urban Projects
- Sudair City: A planned smart city incorporating GIS from the ground up, optimizing infrastructure, zoning, and livability.
- The Line (in NEOM): A futuristic, linear megacity design featuring no cars, carbon-free systems, and services within walking distance. GIS plays a critical role in infrastructure modeling and sustainable vertical urban design.
Urban Expansion & Sustainability Monitoring
- Riyadh: Multiple GIS analyses using Landsat and other satellite data have tracked urban sprawl and vegetation cover. From 2000 to 2022, the built-up area expanded from approximately 654 km² to 1,349 km², while green cover saw fluctuation with recent increases due to sustainability initiatives such as the Riyadh Green Project.
- Jeddah: GIS and remote sensing tools have been used to monitor land-use/land-cover changes, environmental impacts, and urban heat development driven by rapid population growth.
- Mina Valley (Mecca): GIS and DEM-based analyses support flood risk management and urban planning in this spiritually significant and topographically complex area.
- Dammam: A GIS-based urban sustainability assessment highlighted that planning largely emphasized economic concerns, often overlooking social and environmental ones, suggesting more integrated planning is needed.
Informal Settlement Mapping in Riyadh
An approach combining expert knowledge and object-based image analysis (OBIA) achieved 94% accuracy in distinguishing informal settlements vs. formal areas, roads, vegetative zones, and vacant land—demonstrating the precision GIS can offer in urban informal mapping.
Regional GIS Platforms & Observatories
The Urban Observatory project, particularly in the Al-Baha Region, employs GIS to construct unified geographic databases and geospatial monitoring platforms. This supports informed planning, data sharing, and decision-making for sustainable regional growth.
Summary: Key GIS Contributions to Urban Development in Saudi Arabia
| Area of Focus | GIS Application & Impact |
|---|---|
| National geospatial infrastructure | Centralized mapping, real-time urban dashboards, Hajj crowd management |
| Smart city design & modeling | Planning of Sudair City and The Line with walkability and vertical integration |
| Urban sprawl and green monitoring | Tracking expansion over decades, supporting sustainability initiatives |
| Hazard-sensitive planning | Flood protection modeling for areas like Mina Valley |
| Social equity in planning | Mapping informal settlements with high accuracy |
| Regional data ecosystems | Development of geospatial observatories for strategic planning |
Next Steps
If you’d like deeper insights, I’d be happy to explore specific case studies like The Line’s GIS modeling, detailed urban expansion metrics for Jeddah or Riyadh, or even the role of SaudiSat imagery in urban monitoring!

