Interpolation and surface analysis are powerful techniques used in geographic information systems (GIS), environmental science, meteorology, and other fields to estimate unknown values across a geographic area based on known sample data points.
Here’s a breakdown of key concepts and methods:
1. What is Interpolation?
Interpolation estimates values at unknown locations using values from known locations. It’s often used to create continuous surfaces (e.g., temperature, elevation, pollution) from discrete sample data.
2. Common Interpolation Methods
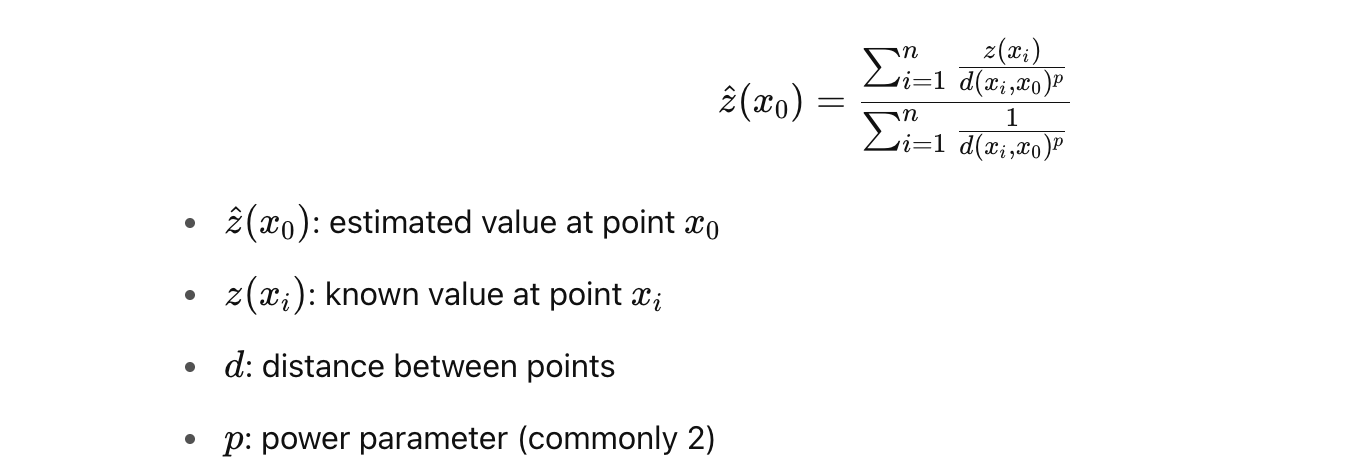
A. Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW)
- Concept: Closer points have more influence on the estimated value than distant points.
- Formula:
- Pros:
- Simple to implement
- Fast
- Cons:
- Assumes spatial autocorrelation
- No estimation of prediction error
B. Kriging
- Concept: A geostatistical method using spatial autocorrelation to make optimal, unbiased predictions.
- Types:
- Ordinary Kriging: assumes a constant unknown mean
- Universal Kriging: accounts for a trend (e.g., slope)
- Indicator Kriging: for binary or categorical data
- Steps:
- Calculate semivariogram (a function describing spatial dependence).
- Fit a model to the semivariogram (e.g., spherical, exponential).
- Use model to estimate values and prediction uncertainty.
- Pros:
- Produces optimal estimates
- Provides error estimates (kriging variance)
- Cons:
- Complex and computationally intensive
- Assumes stationarity (can be relaxed with advanced forms)
C. Other Methods
- Spline: Smooth surface that minimizes curvature.
- Natural Neighbor: Uses Voronoi diagrams for interpolation.
- Trend Surface: Fits a polynomial to data (not good for localized variation).
3. Applications of Surface Analysis
- Environmental Monitoring: Air/water quality, rainfall
- Agriculture: Soil fertility, crop yield estimation
- Geology: Mineral exploration, terrain modeling
- Urban Planning: Noise pollution, accessibility
4. Choosing Between IDW and Kriging
| Feature | IDW | Kriging |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low | High |
| Assumes Spatial Autocorrelation | Yes | Yes (explicitly modeled) |
| Error Estimation | No | Yes |
| Data Requirements | Moderate | High (requires modeling semivariance) |
| Speed | Fast | Slower |

